How much protein do we need to eat every day?
How much protein should we be eating every day? Well, that depends!
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) or recommended minimum amount (RMA) for the average healthy sedentary adult is 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight per day (0.36g/pound). This is the amount that is required to avoid malnutrition, but short of what might be regarded as optimum.
Recommended minimum (RDA) amounts:
72 grams of protein per day for the average sedentary man (bodyweight of 90 kg/198 pounds)
60 grams of protein per day for the average sedentary woman (bodyweight of 75 kg/165 pounds)
(Yes, evidently 75 kg and 90 kg are the average body weights for women and men respectively in the U.S.)
This amount may be enough to prevent deficiency, but it’s far from enough to ensure optimal health and body composition. These recommendations were based on nitrogen balance studies and are called the Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDCAAS). Newer amino acid oxidation techniques are much more indicative of protein requirements using the Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score (DIAAS). By using these techniques, the RDA minimum for an adult, and younger middle-aged person is 1.2 to 1.5 grams per kilogram or 0.55 to 0.68 grams per pound of bodyweight of protein per day.
Actual minimum amounts to (remember – still minimum, not optimum):
108-135 grams of protein per day for the average man (bodyweight of 90 kg/198 pounds)
90-113 grams of protein per day for the average woman (bodyweight of 75 kg/165 pounds)
These minimums also don’t consider conditions that impact the absorption of protein, such as H. pylori, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO), low-grade inflammation etc., and protein quality and bioavailability.
Looking at the amount of protein needed to thrive, if you are active and prevent age-related muscle loss, you are likely to need 2.2 grams per day per kilogram or 1 gram per pound of body weight per day.
Reasonable amounts to “thrive”:
198 grams per day for the average man (bodyweight of 90 kg/198 pounds)
165 grams per day for the average woman (bodyweight of 75 kg/165 pounds)
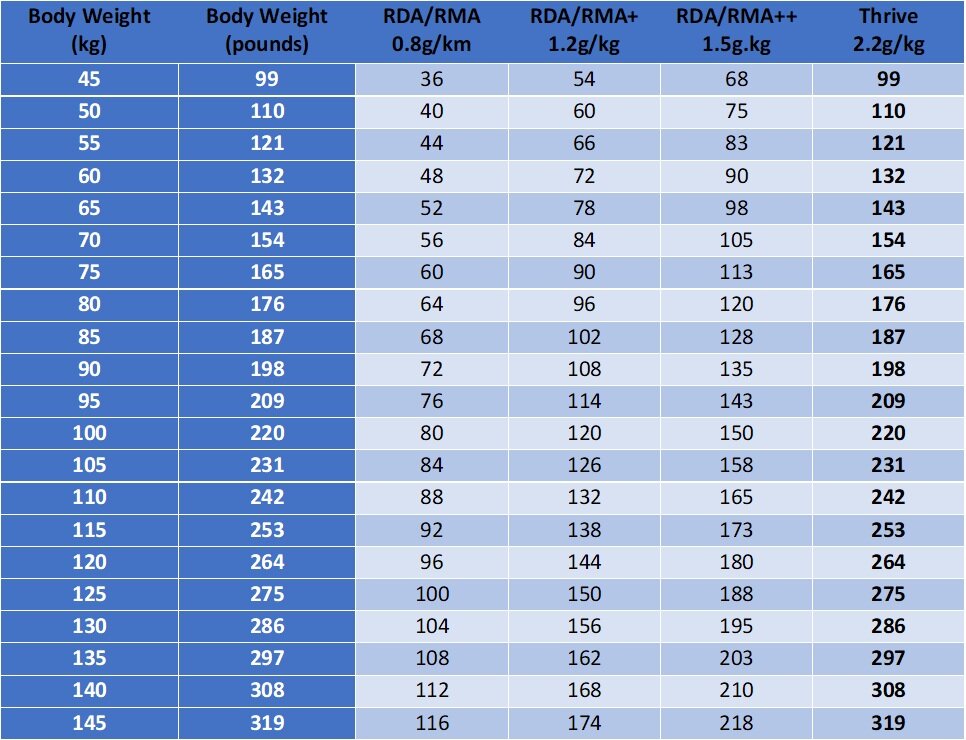
How much protein do you need to eat every day for your body weight?
RMA-Recommended Minimum Amount
RMA+ & RMA++-RMA using amino acid oxidation techniques
One of the things to consider in the protein equation is the quality of the protein and especially the amount of the branched-chain amino acid called leucine it contains. The recommended daily allowance of 2-3 grams per day to protect against disease. The reality of thriving and maintaining muscle mass is closer to 8-9 grams per day distributed at 2.5-3 grams per meal in a day. In other words, to protect your muscle tissue from loss, especially as you age (sarcopenia), your body requires higher amounts of high-quality protein distributed throughout the day to generate an anabolic response (protein synthesis to repair and grow muscle tissue). Also, keep in mind that the most demanding essential amino acid requirements are for infants with potentially double the leucine requirements of adults.
The question comes up if you can do this as a vegan or vegetarian. Yes, you can, but it would be challenging, complicated, and you would have to spend a lot of time and effort into doing it.
Beef & Plant Protein Amino Acid Profiles
Beef contains more of every single essential amino acid than every plant protein apart from soybeans, which are slightly higher in tryptophan. In the case of leucine, the difference is significant. The digestibility is also affected by the form of the protein. The digestibility of plant protein decreases the less processed it is. The digestibility values of plant proteins are about 70% to 90%, vs. casein, and egg, which have a digestibility value of 97% or above. The recommendation is that vegans and vegetarians consume an additional 10% to 20% protein to compensate for digestibility while keeping in mind the lack of essential amino acids in many plant proteins.
The other difficulty with only eating plant proteins is maintaining the basic RDA for calcium, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), retinol, vitamin B12, and likely zinc, vitamin K2, vitamin A, and other micronutrients. It would be easy to eat 300 grams plus carbohydrates a day trying to meet all the nutrient requirements with plant protein and the problems that would result in doing so, such as diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
Therefore, to be able to thrive using a plant protein diet is possible, but it is very complicated to make it work and maintain.